Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; Xu, P. G.; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Yin, F.*
Scripta Materialia, p.116046_1 - 116046_6, 2024/05
Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Engineering, Mechanical)Hydrogen(H) embrittlement in high-strength aluminum(Al) alloys is a crucial problem. H accumulation at the interface of precipitates in Al alloy is considered to cause embrittlement. However, there is no quantitative knowledge regarding the interaction between H distribution and stress field near cracks. In this study, using a multi-modal three-dimensional image-based simulation combining the crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis, we tried to capture the stress distribution near the crack, its influence on the H distribution, and the probability of crack initiation in the experimental condition. As a result, it was found that grain boundary cracks transition to quasi-cleavage cracks in the region where the cohesive energy of the semi-coherent interface of MgZn precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Cl dissociation, CH
Cl dissociation, CH abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH
abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)
Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)Makino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 642, p.158568_1 - 158568_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Xu, P. G.; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 23 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Higa, Ryota*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
Keikinzoku, 73(11), p.530 - 536, 2023/11
In Al-Zn-Mg alloys, suppression of hydrogen embrittlement is necessary to improve their strength. In this study, the distribution of stress, strain, and hydrogen concentration in the actual fracture region was investigated using the crystal plasticity finite element method and hydrogen diffusion analysis based on a model derived from three-dimensional polycrystalline microstructural data obtained by X-ray CT. In addition, the distributions of stress, strain, and hydrogen concentration were compared with the actual crack initiation behavior by combining in-situ observation of tensile tests using X-ray CT and simulation. The results show that stress loading perpendicular to the grain boundary due to crystal plasticity dominates grain boundary crack initiation. It was also found that internal hydrogen accumulation due to crystal plasticity has little effect on crack initiation.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Materials Transactions, 64(11), p.2553 - 2559, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We attempted to calculate the hydrogen trapping energies on the incoherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates and Mg
precipitates and Mg Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg
Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg Si in the aluminum matrix.
Si in the aluminum matrix.
 MnGa metamagnetic shape memory alloy with small energy loss
MnGa metamagnetic shape memory alloy with small energy lossIto, Tatsuya; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*
Busseiken Dayori, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Yoichi*; Umemoto, Yoshihiko*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Hashimoto, Yuki*; Kitazawa, Takafumi*; Fujita, Masaki*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Liss, K.-D.*; Xu, P. G.; Shiro, Ayumi*; Zhang, S. Y.*; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Akita, Koichi*
Advanced Engineering Materials, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Liu, X. J.*; Xu, P. G.; Shiro, Ayumi*; Zhang, S. Y.*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Akita, Koichi*; Zolotoyabko, E.*; Liss, K.-D.*
Journal of Materials Science, 57(46), p.21446 - 21459, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Xu, X.*; Odaira, Takumi*; Xu, S.*; Hirata, Kenji*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Ueki, Kosuke*; Ueda, Kyosuke*; Narushima, Takayuki*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*; et al.
Advanced Materials & Processes, 180(7), p.35 - 37, 2022/10
Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Hagihara, Koji*; Watanabe, Masashi*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 10(5), p.438 - 446, 2022/10
no abstracts in English
Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; Machida, Akihiko*; Watanuki, Tetsu*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Mizuno, Masataka*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Acta Materialia, 234, p.118055_1 - 118055_10, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:81.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tsuda, Yasutaka; Gueriba, J. S.*; Ueta, Hirokazu*; Di o, W. A.*; Kurahashi, Mitsunori*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Kurahashi, Mitsunori*; Okada, Michio*
JACS Au (Internet), 2(8), p.1839 - 1847, 2022/08
Odaira, Takumi*; Xu, S.*; Hirata, Kenji*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Ueki, Kosuke*; Ueda, Kyosuke*; Narushima, Takayuki*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Harjo, S.; et al.
Advanced Materials, 34(27), p.2202305_1 - 2202305_11, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:87.92(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Yamauchi, Akihiro*
JAEA-Research 2022-001, 21 Pages, 2022/06
The primary cause of cladding embrittlement during loss-of-cool ant accident (LOCA) is the increase in oxygen concentration in the metallic layer and associated microstructural change due to oxidation. In the case of cladding high temperature rupture, inner surface oxidation by the steam ingress and the consequent increase in hydrogen partial pressure result in hydrogen absorption (secondary hydriding) localized in the axial direction at the distance apart from the rupture opening as is well known from preceding studies. In order to understand the effect of cladding microstructural changes on mechanical property of a fuel rod under LOCA conditions in a more precise and quantitative manner, the nanoindentation method has been applied to evaluation of mechanical properties of a cladding specimen after a LOCA simulated test; results for two samples taken from the rupture opening part and secondary hydriding part were compared with each other. The fraction of plastic work during the indentation was evaluated from the load-displacement curve in addition to hardness and Young's modulus. The plastic work fraction at the secondary hydriding part was found to be clearly lower than that at the rupture opening part and rather close to that in the ZrO and
and  -Zr(O) layers, suggesting the significant ductility reduction of the secondary hydriding part despite its relatively low oxygen concentration.
-Zr(O) layers, suggesting the significant ductility reduction of the secondary hydriding part despite its relatively low oxygen concentration.
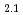 during high temperature deformation
during high temperature deformationJaladurgam, N. R.*; Lozinko, A.*; Guo, S.*; Harjo, S.; Colliander, M. H.*
Materialia, 22, p.101392_1 - 101392_4, 2022/05